Warning: If you have upgraded from 2.7.X to 3.X on Windows, please be aware that
user names are now case sensitive.
Your Aspera server uses your system accounts to authenticate connections. These
system accounts must be added and configured before attempting an Aspera transfer.
When creating transfer accounts, you may also specify user-based settings, including
those for bandwidth, document root (docroot) and file handling.
Note: You must create systems accounts for transfer users before they can be
configured on your Aspera server. After these system accounts have been created
and initialized on your local host, follow the steps below to configure their
transfer accounts.
-
Add a system user to your Aspera server.
Launch the application () and click Configuration.
In Server Configuration, select the Users tab and
click the  button.
button.
-
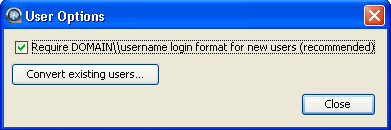
Enter user's name and optional domain, and set login requirement.
Within the "Add User" box, input the user's name and optional domain,
then click OK. Note that for domain users, you can
set a requirement that they must log into their accounts using the
DOMAIN\username format (which is also recommended by Aspera). To
set this requirement, click the Options... button
under the Users tab in the Server
Configuration window. Enable the checkbox to set the requirement for
new users and/or click the Convert existing users...
button to set the requirement for existing domain accounts.
Note: You cannot add a username with an "@" symbol, except when using the
"user@domain" format. For additional information, please view the topic
"Product
Limitations."
-
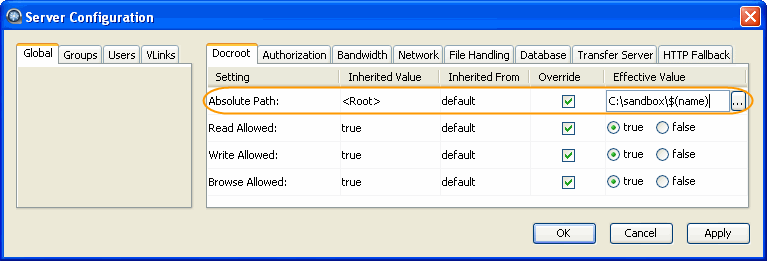
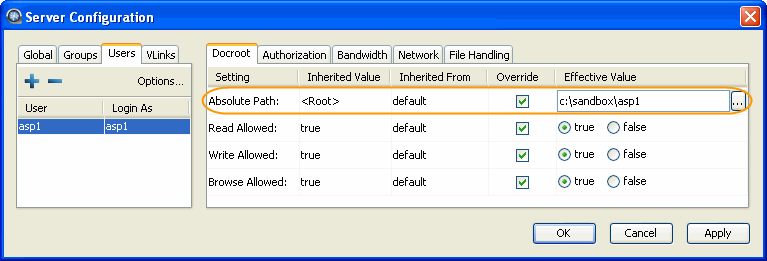
Set up user's docroot.
You can limit a user's access to a given directory using the document root
(docroot). To set it up, click
Configuration>UsersusernameDocroot.
Check the Override box for Absolute Path and
enter or select an existing path as the user's docroot -- for example, C:\sandbox\asp1
. Make sure that at least the
Read Allowed and Browse Allowed are set to true.
Click OK or Apply when
finished.
If there is a pattern in the docroot of each user, for example, C:\sandbox\username, you can take advantage of a
substitutional string. This allows you to assign an independent docroot to
each user without setting it individually for each user.
| Substitutional String |
Definition |
Example |
| $(name) |
The system user's name. |
C:\sandbox\$(name) |
| $(DOMAIN) |
The domain user's domain name. |
C:\sandbox\$(DOMAIN)\$(name) |
Set up a docroot with a substitutional string as follows: in the Server
Configuration dialog, select the Global tab and the
Docroot tab, and enter the docroot into the
Absolute Path field. This value will be duplicated in all user
settings.