Introduction
IBM Aspera fasp.io is a lightweight software component for high-speed bidirectional data transport. Using the patented Aspera FASP protocol, fasp.io achieves speeds of up to 2.5 Gb/sec over unmanaged networks.
Aspera fasp.io fully utilizes available bandwidth to transfer data in byte-order sequence at the maximum possible speed with near-zero latency. It removes the barriers of size, distance, and complexity to move data between on-premises and cloud infrastructures.
Aspera fasp.io provides significant improvements in performance and service quality when transferring data between highly remote or dispersed locations in unfavorable network conditions, such as high latency and packet loss.
IBM Aspera extends its existing data transfer software portfolio with a new option, the Aspera fasp.io Gateway. Gateway is a software component that can be integrated quickly and easily with existing applications that use a TCP connection for their data flow. It improves nearly all server-to-server TCP-based data flows regardless of the distance and network conditions.
The IBM Aspera fasp.io Gateway acts as a transport layer proxy between TCP and Aspera FASP.
Usage
Gateway Client/Server Usage
In this configuration, two fasp.io Gateways are used to bridge one (or several) TCP connections from TCP clients to a TCP server over FASP:
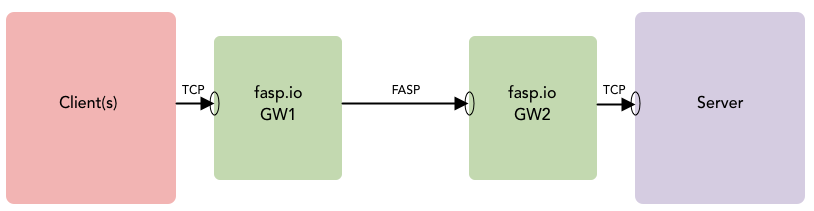
Given a Server listening on port 12345, configure your client to point to the fasp.io Gateway 1 (GW1 IP) and port 12345:
[[bridge]]
[bridge.local]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 12345
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "GW2"
port = 12345fasp.io GW2 Configuration
[[bridge]]
[bridge.local]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 12345
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "Server"
port = 12345
Gateway Server/Server Usage
For some use cases, such as DB replication or messaging services (like MQ or Event Streams), communication must be established by both sides. In this mode, each server initiates a connection to the other:

[[bridge]]
name = "Outbound"
[bridge.local]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 12345
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "GW2"
port = 12345
[[bridge]]
name = "Inbound"
[bridge.local]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 54321
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "Server1"
port = 54321[[bridge]]
name = "Outbound"
[bridge.local]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 54321
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "GW1"
port = 54321
[[bridge]]
name = "Inbound"
[bridge.local]
protocol = "fasp"
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 12345
[bridge.forward]
protocol = "tcp"
host = "Server2"
port = 12345