Introduction
HST Server can be deployed as a high-availability cluster. This is done by configuring a Redis database cluster and using HAProxy to connect the HST Servers to the Redis database. The Redis and HAProxy applications are included in your HST Server installation.
Overview
Deploying HST Server as a high-availability cluster enables you to leverage the high-speed transfer capabilities of Aspera with continuous availability and automatic failover if one node goes down.
A cluster consists of nodes. A node is a machine (physical, virtual, or container) on which IBM Aspera High-Speed Transfer Server and Redis are installed. A Redis node can be a primary (also called a "master") or replica ("slave").
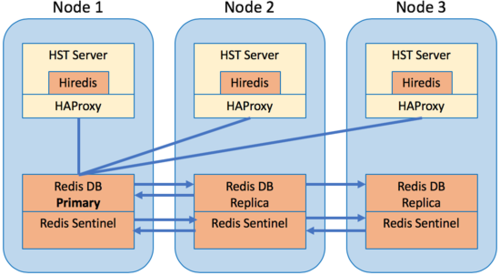
Cluster Architecture
In an HST Server cluster with a highly-available Redis backend:
- Each node has HST Server, Redis, and HAProxy. HST Server uses the Redis database to manage security and transfers. In a cluster configuration, all HST Servers use the Redis database on the primary node, which is cloned to the replica nodes.
- HST Server uses Hiredis, a Redis client, to interact with the Redis database.
- To direct Hiredis requests from all the HST Servers to the primary Redis node, the cluster uses HAProxy, a TCP proxy, to identify which Redis nodes are running and which is the master.
- Redis Sentinel monitors the status of the Redis databases, communicates between Redis nodes, and automatically promotes a replica to primary if the primary is failing.
Features and Limitations
Features:
- Robust, reliable database software that is included as part of your HST Server installation.
- Automatic failover from primary to replica.
- Eventual consistency.
Limitations:
- Requires at least three nodes.
- Does not load-balance transfers between HST Servers.
- Does not shard data between Redis nodes.
- Does not support bi-directional replication with conflict resolution.