Public key authentication (SSH Key) is a more secure alternative to password
authentication that allows users to avoid entering or storing a password, or sending it over
the network. The client creates an SSH key pair (a public key and a private key) and then
sends the public key to the server's administrator. Once the admin configures the server
with the client's public key, the client can authenticate connections to the server with
their private key.
You can use the application GUI to generate key pairs and to import existing key pairs. You
can also generate key pairs using the command line; for instructions, see Creating SSH Keys (Command Line).
-
Launch the application.
-
In the menu bar, click Tools > Manage Keys.
-
In the SSH Keys dialog, click
 to create a new key pair.
to create a new key pair.
![Click [Add] in the SSH Keys window.](../images/linux/pubkey.png)
The SSH Keys dialog is also available from the
Connection tab in the Connection Manager. When
you select Public Key for authentication, the
Manage Keys button appears; clicking it opens the
SSH Keys dialog.
-
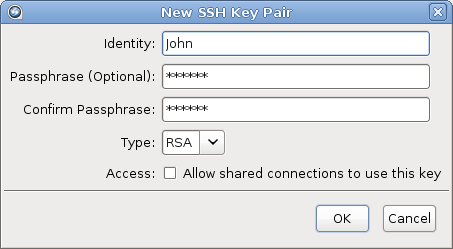
In the New SSH Key Pair window, enter the requested
information.
| Field |
Description |
| Identity |
Name your key pair, such as with your user name. |
| Passphrase |
(Optional) Set a passphrase on your SSH key, which will be
prompted for whenever it needs to use the key. If you don't want the
user to be prompted for passphrase when logging in, leave this field
blank. |
| Type |
Select RSA (default) or ECDSA key. |
| Access |
When sharing a connection with public key authentication, or a
connection that is has a Hot Folder (on Windows machines), this
option must be checked. |
-
Click OK to create the key.
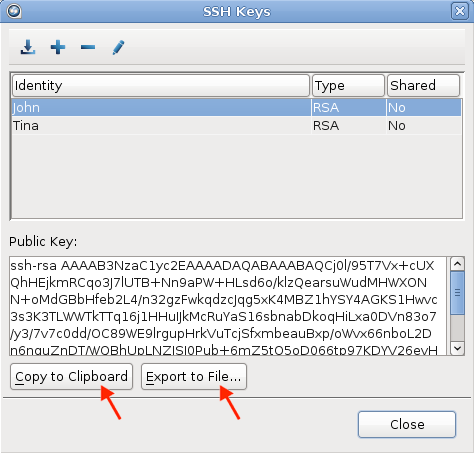
The public key is displayed in the window and you can copy it to a clipboard
or export it to a file that is easy to locate. The key is automatically
saved as a file named
id_key_type.pub in the following
location (in the example below, the public key filename is
id_rsa.pub):
/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
-
Distribute the public key.
Provide the public key file to your server administrator so that it can be set
up for your server connection.
To copy or export the public key, select the
key in the SSH Keys window, click Copy
Public Key to Clipboard, and paste the string into an email
to send to the server administrator, or click Export to
File and save the public key as a file.
For information on how to install the public key on the
server, see Setting Up a User's Public Key on the Server; however,
the server may be installed on a different operating system from the
client.
-
Set up connections using public key authentication.
Note: Your public key must be configured on the server before you can connect
with it.
-
Click Connections to open the Connection
Manager.
-
Select the connection for which you want to set up the key.
-
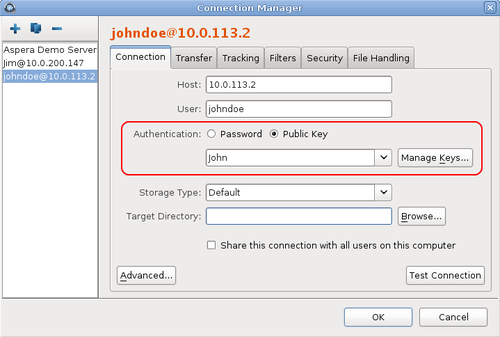
In the Connection tab, select the
Public Key Authentication option and select
the key from the drop-down menu.
Note: When you are sharing a connection with
public key authentication (
Share this connection with all
users on this computer is selected), the SSH key
should be shared as well. You can edit an existing key by opening
the
SSH Keys window. In the SSH Keys dialog,
select a key and click the
button to open the
Edit SSH
Key Pair dialog. Select
Allow shared
connections to use this key. Shared keys are moved
to the Aspera
etc directory.
Importing keys:
To import keys created outside the GUI, go to Tools > Manage
Keys to open the SSH Keys dialog. Click the
 button in the upper-left corner of the dialog to open a file browser. You can import
the key pair by selecting either the private key or the public key; this will copy
both keys into the user's .ssh directory. You cannot import a key pair if a
key pair with the same identity already exists in the .ssh directory.
button in the upper-left corner of the dialog to open a file browser. You can import
the key pair by selecting either the private key or the public key; this will copy
both keys into the user's .ssh directory. You cannot import a key pair if a
key pair with the same identity already exists in the .ssh directory.
Imported key pairs can be shared with other users. In the SSH Keys dialog, select a key and
click the  button to open the Edit SSH Key
Pair dialog. Select Access to allow shared
connections to use this key. Shared keys are moved to the Aspera
etc directory.
button to open the Edit SSH Key
Pair dialog. Select Access to allow shared
connections to use this key. Shared keys are moved to the Aspera
etc directory.
 button in the upper-left corner of the dialog to open a file browser. You can import
the key pair by selecting either the private key or the public key; this will copy
both keys into the user's .ssh directory. You cannot import a key pair if a
key pair with the same identity already exists in the .ssh directory.
button in the upper-left corner of the dialog to open a file browser. You can import
the key pair by selecting either the private key or the public key; this will copy
both keys into the user's .ssh directory. You cannot import a key pair if a
key pair with the same identity already exists in the .ssh directory. button to open the Edit SSH Key
Pair dialog. Select Access to allow shared
connections to use this key. Shared keys are moved to the Aspera
etc directory.
button to open the Edit SSH Key
Pair dialog. Select Access to allow shared
connections to use this key. Shared keys are moved to the Aspera
etc directory. 
![Click [Add] in the SSH Keys window.](../images/linux/pubkey.png)