The following pre-processing and post-processing script examples demonstrate how Aspera
prepost environment variables are used to achieve different types of processing.
These examples use bash syntax. To run these examples on your own system, do the
following:
-
Shell - Change file and directory permissions.
In the shell script, change file and directory permissions after receiving, and log
into the file /tmp/p.log:
#!/bin/bash
if [ $TYPE == File ]; then
if [ $STARTSTOP == Stop ]; then
echo "The file is: $FILE" >> /tmp/p.log
chmod 777 $FILE
fi
fi
-
Shell - Forward files to another computer.
In the shell script, transfer received files to a third computer 10.10.10.10, and
remove the local copy.
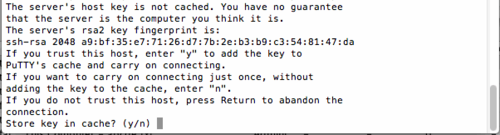
Important: For this example to work properly, the server's host key must be
cached.
#!/bin/bash
TARGET=aspera@10.10.10.10:/tmp
RATE=10m
export ASPERA_SCP_PASS=aspera
if [ $TYPE == File ]; then
if [ $STARTSTOP == Stop ]; then
if [ $STATE == success ]; then
if [ $DIRECTION == recv ]; then
logger -plocal2.info "Move file $FILE to $TARGET"
ascp -T -o RemoveAfterTransfer=yes -l $RATE $FILE $TARGET
fi
fi
fi
fi
-
Shell - Create a log of successfully transferred files.
In the shell script, store successfully transferred files as a list into the file
/tmp/aspera.transfer.log:
#!/bin/bash
if [ $TYPE == File ]; then
if [ $STARTSTOP == Stop ]; then
if [ $SIZE -gt 0 ]; then
if [ `expr $SIZE - $STARTBYTE` -gt 0 ]; then
echo `date` >> /tmp/aspera.transfer.log
echo "$STATE $FILE $SIZE bits transferred" >> /tmp/aspera.transfer.log
fi
fi
fi
fi
