To avoid specifying S3 storage credentials in a docroot, you can use your AWS
Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles to set docroots to S3 storage. The steps
below assume the following:
- You have purchased and booted up your Aspera On Demand product.
- You have created an S3 bucket.
- You have permissions to create IAM roles or change the policies of your
IAM.
- You know how to SSH as root to your Aspera On Demand instance
-
Log into AWS Management Console as admin and create a new IAM
role that has access to your S3 storage.
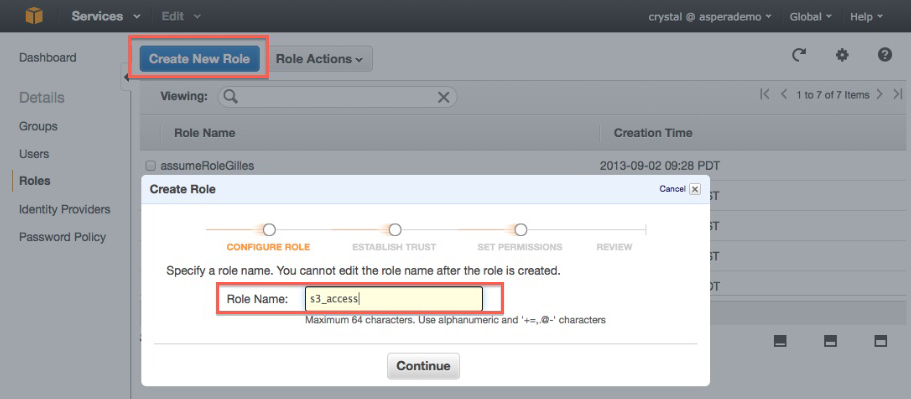
Click the Create New Role button. In the Create Role
dialog that appears, fill in a role name (s3_access in the following
screen), and click Continue.
-
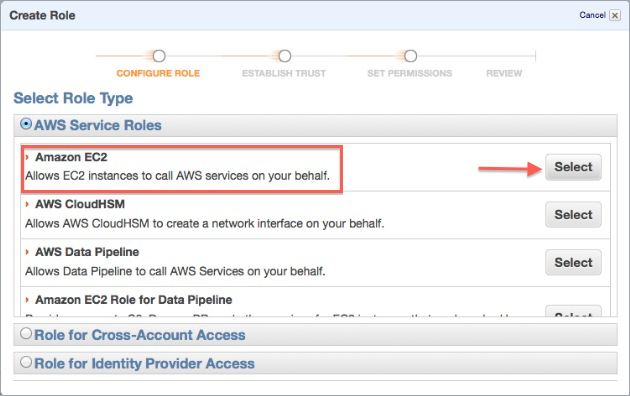
On the Select Role Type panel, choose AWS Service Roles, and select the
Amazon EC2 role type.
-
On the Set Permissions panel, choose Select Policy Template, and select the
Amazon S3 Full Access policy template.
The policy can be modified later.

Alternatively, you can set policy by choosing the Policy
Generator. For example, the following sets permissions that allow all
actions on all S3
resources:
{
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1360956435483",
"Action": [
"s3:*"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
The
following is a Trust Relationships sample for EC2. The date conditions are
optional.
{
"Version": "2008-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Condition": {
"DateLessThan": {
"aws:CurrentTime": "2033-02-18T13:00:00.000+0000"
},
"DateGreaterThan": {
"aws:CurrentTime": "2010-08-16T12:00:00.000+0000"
}
}
}
]
}
-
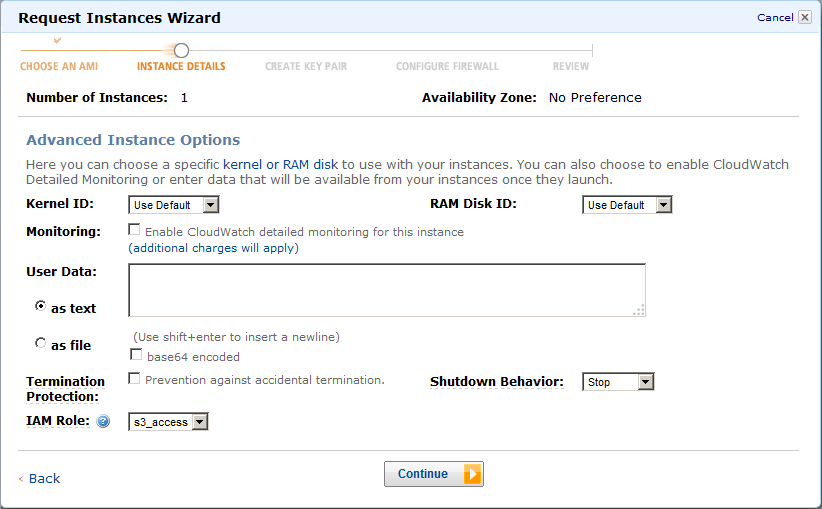
Launch an AMI using the IAM role that has access to S3 storage.
-
Connect to your server through SSH as root.
# ssh -i identity_file -p 33001 ec2-user@ec2_host_ip
# sudo su -
-
Modify aspera.conf or use the Aspera Console UI to set the transfer
user's docroot.
<user>
<name>ec2-user</name>
...
<absolute>s3://s3.amazonaws.com/s3-bucket-name</absolute>
...
</user>
Restart asperanoded:
# /etc/init.d/asperanoded restart



