This documentation walks you through how to set up a FASPStream connection
between two machines, start a multicast with an encoded transport stream, test that
the receiving machine is receiving packets, and play the streamed media
content.
The following instructions requires two machines installed with FASP
Stream:
- Machine A: Linux machine with the built-in sender license.
- Machine B: Linux machine with a receiver license.
The following steps must be performed on Machine A:
-
Start ascp4 to transport streams when an input is
available.
The following example assumes you have SSH key access to Machine B from
Machine
A.
$ ascp4 --mode=send --user=machineB_user -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa --host=machineB --compression=none --read-threads=1 --write-threads=1 udp://233.3.3.3:3000?loopback=1&ttl=2 udp://233.4.4.4:4000?loopback=1&ttl=2
-
Download a test file to stream.
In your browser, download the
ed24p_00.zip test file from
the www.w6rz.net website (a community transport stream testing website):
http://www.w6rz.net/ed24p_00.zip
Extract the contents into
an easily accessible folder. You may provide your own media file, but the
examples in this documentation assume that you are using the
ed24p_00.zip transport stream file located at
/temp/ed24p_00.ts.
-
Provide a multicast stream of a test file to ascp4.
The following example uses the third-party, open-source
ffmpeg command. If you do not have
ffmpeg on your machine,
$ sudo apt-get install lib-avtools
Run the
ffmpeg command with the location of the media
file and set the URI of the resulting
stream:
$ ffmpeg -re -i /temp/ed24p_00.ts -vcodec copy -acodec copy -f mpegts "udp://233.3.3.3:3000?ttl=2&pkt_size=1316"
-
Check to see the output of ascp4 to make sure the Rate of
transfer is going up to the expected speed.
Now that your stream is running and ascp4 shows that it
is transporting the stream, check the receiver is receiving the media file. The
following steps must be performed on Machine B:
-
Run the tcpdump command to check streams are coming.
The port number corresponds to
port configured in the destination multicast URI. In the example below, the
destination port was configured as
4000.
$ sudo tcpdump upd and port 4000
-
Play the media file over the stream.
The following example uses the third-party, open-source
vlc
command. If you do not have
vlc on your machine,
run the following command:$ sudo apt-get install vlc-nox
Using
VLC, play the media from the stream.
-
Open VLC.
-
Click Open media. In the resulting dialog, go to
the Network tab and click Open RTP/UDP
Stream.
-
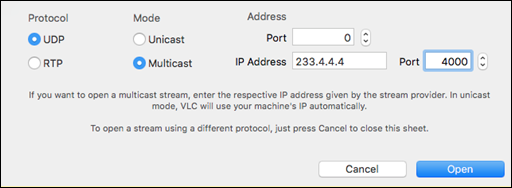
Configure the settings according to your multicast URI.
| Option |
Value |
| Protocol |
UDP |
| Mode |
Multicast |
| IP Address |
233.4.4.4 |
| Port (for the IP Address) |
4000 |
Your media file should now be playing in the VLC media player.
